Common Tools in CNC Machining, Different Tools
Correspond to Different Product Processing
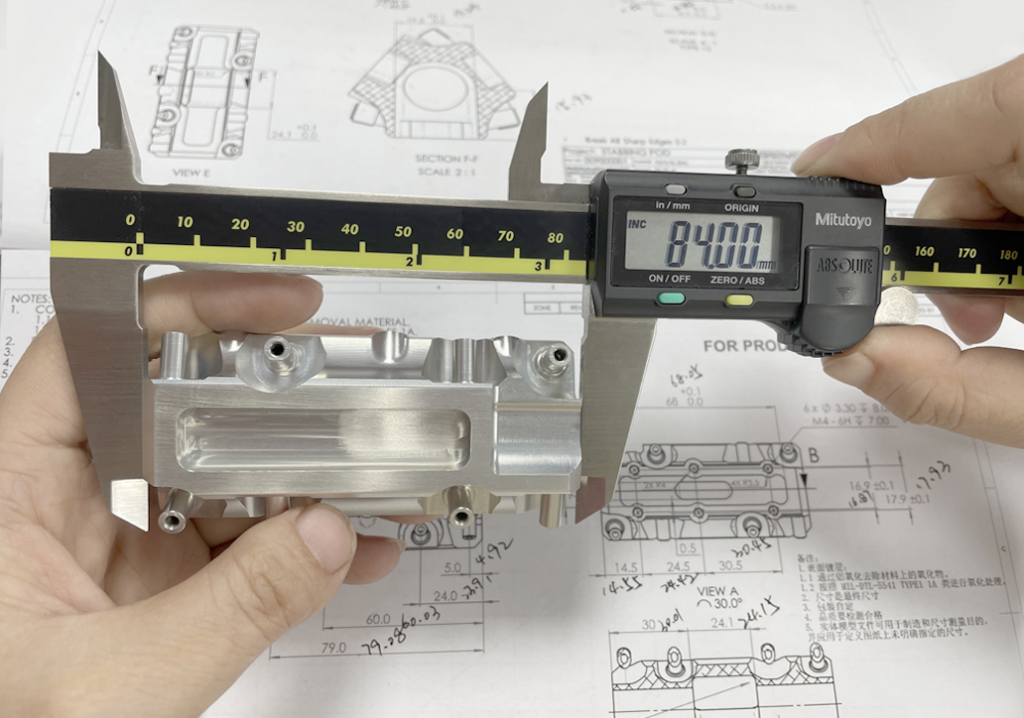
Posted on:April 8th,2024 By GREFEE
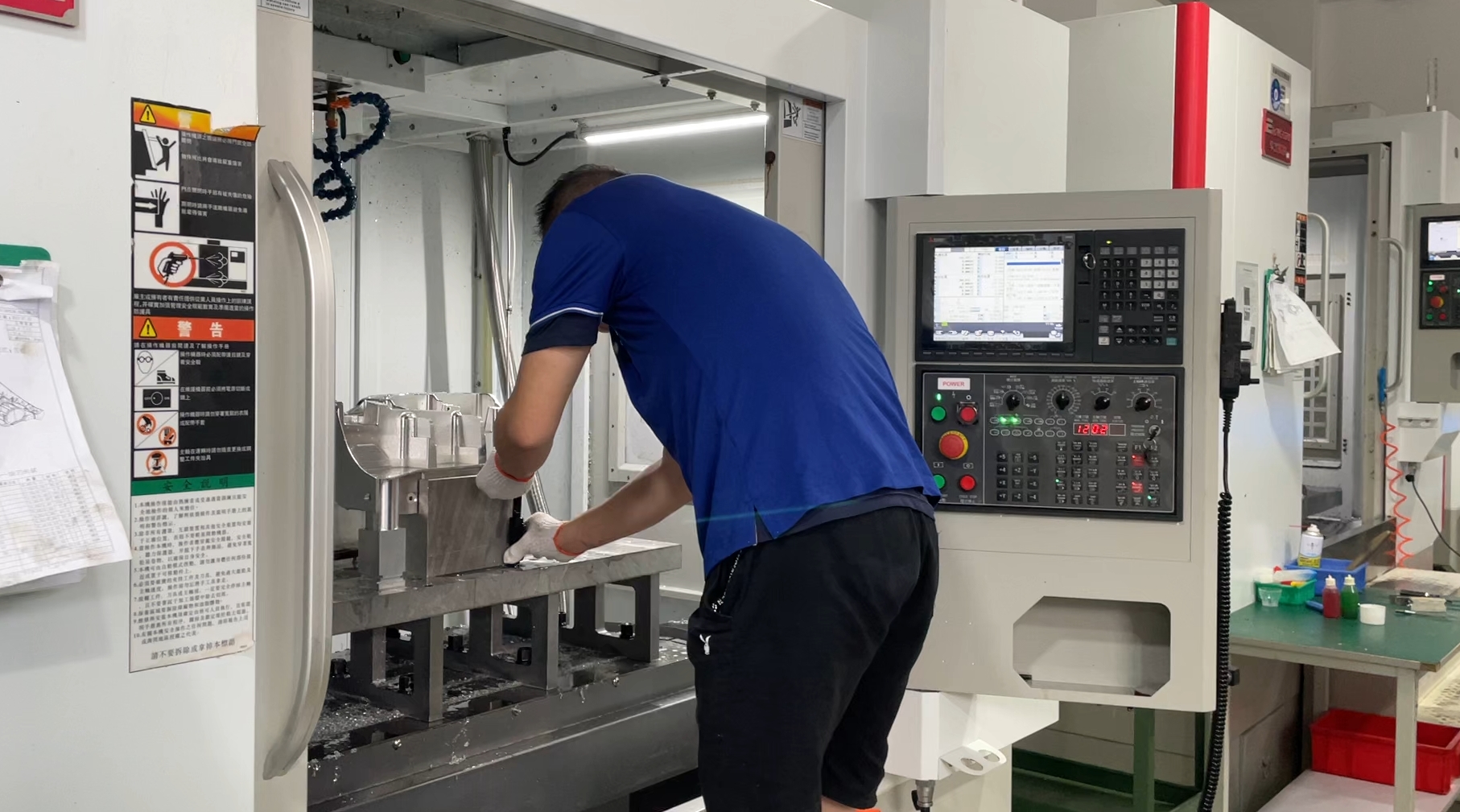
CNC machining belongs to the category of metal cutting, but has its own characteristics.
Realized as a highly automated, long-running continuous machining process in which tool setup times are more complex and time-consuming than conventional machining, there are many issues to consider when selecting tools.
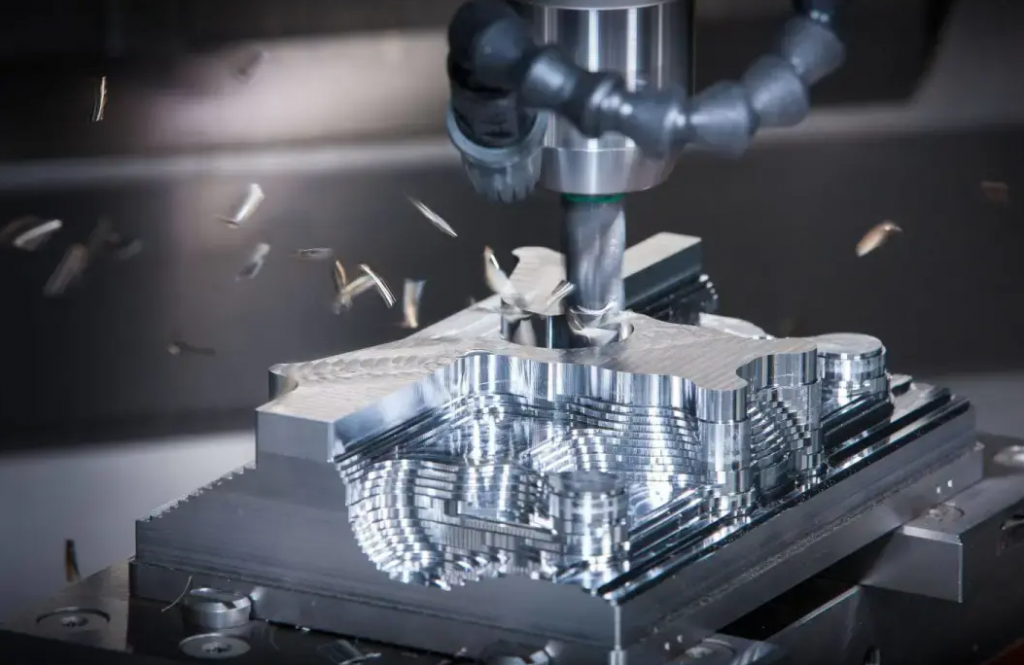

Ⅰ、Mold materials and coatings
The various tool materials in use today have properties suited to different machining requirements.
Properties required for common tool materials include a low coefficient of friction, high accuracy, good thermal conductivity, adequate toughness and impact resistance.
Commonly used tool materials for conventional CNC machine tools are high-speed steel and carbide.
However, in special cases such as high-speed cutting, dry cutting, cutting difficult-to-machine materials, and turning instead of grinding, superhard materials such as ceramics, CBN, PCBN, and diamond are required. These superhard materials are relatively expensive, the cutting process and parameters are not easy to learn, and there are certain requirements for the rigidity of the machine tool.

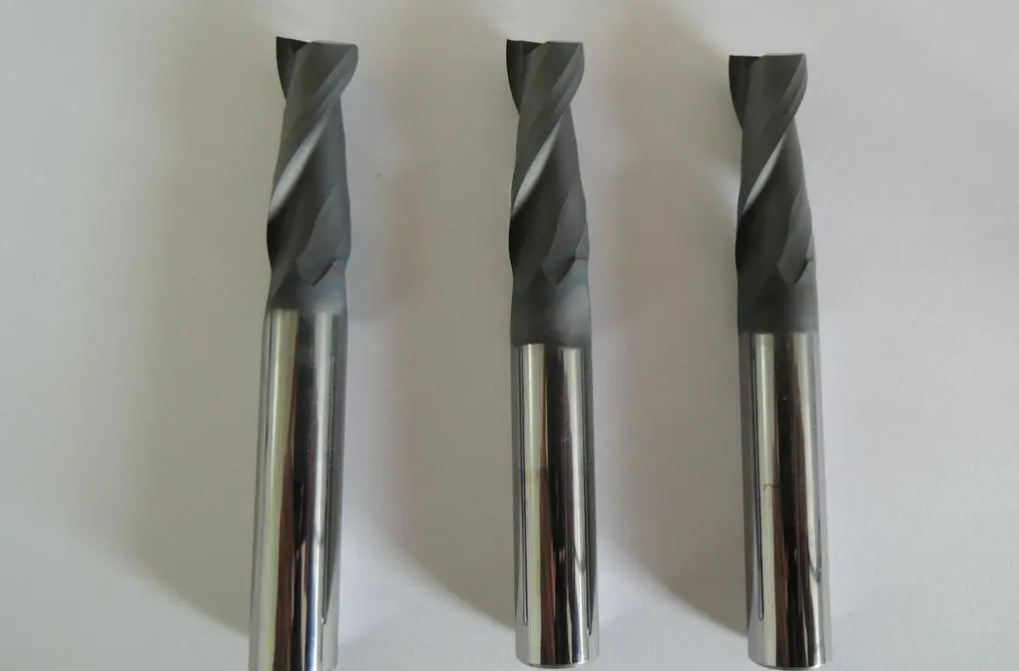
II. Carbide material tools
Tool surface coating is one of the most important ways to improve tool performance.
Coated tools last up to 10 times longer than uncoated tools and common coatings include Titanium Nitride TIN, Titanium Carbide Nitride TICN and Aluminum Oxide.

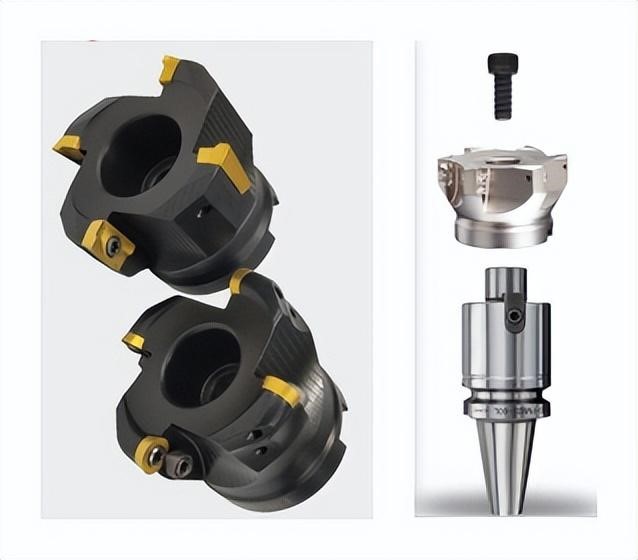
III. Tool classification
CNC commonly used tools are roughly divided into, large flying knife (D80R6), round nose knife (D17R0.8), flat bottom knife (D10), ball knife (R3) and other (chamfering knife, dovetail knife, maize knife, T-shaped knife, hit the point of the knife, carving knife, T tooth knife) and so on.
1.milling cutter (D80R5, D80R6, D80R0.8, D80R2, etc.)
Main uses: flying surface, glossy surface, large range of roughing (open large roughing).

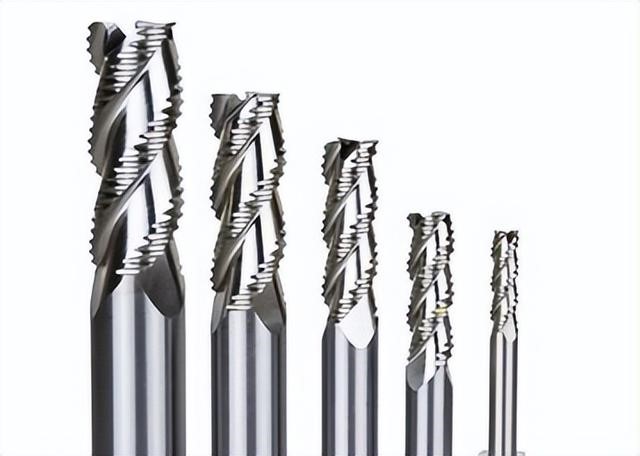
2.Round nose knife, referred to as flying knife (D17r0.8,D21r0.8,D17R2 etc.)
Main purpose: open rough, clear angle, such as high-gloss knife.

3.Flat bottom knife (D16,D10,D6,D4)
Main purpose: open rough, clear angle, light wall light bottom. Characteristics: flat enough, straight body, sharp blade.
The left one is alloy knife, tungsten steel knife, coated knife. Mainly used for processing hard materials, such as 45 steel, P20, etc.

4.Roughing cutter for aluminum (preferred for dynamic milling)
Main application: roughing
Characteristics: side edges are more worthy of development than bottom edges.
Main processing: aluminum

5.White steel knife
Main uses: tread countersunk head is quite good.
Features: longer blade, sharper edge, lower price.
Main process: aluminum, copper, plastic and other materials with slightly lower hardness.
6.Ball cutter (D10R5,D6R3,D2R1)
Main applications: arc surface, beveled surface, milling runners, lettering, engraving, chamfering.
Characteristics: round head, processing to be high speed, small steps.
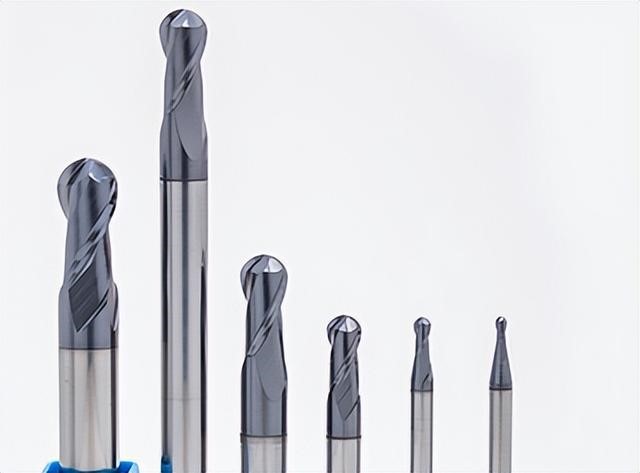

7.Center drill (pointing cutter)
Main purpose: to hit the point and set the position.

8.Center drill (pointing cutter)
Main purpose: to hit the point and set the position.
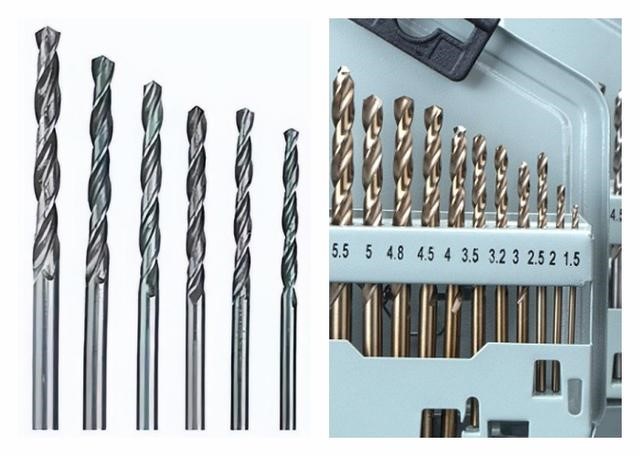

9.U-drill (explosive force drill)
Main uses: pre-drilling, stock removal, deep holes.
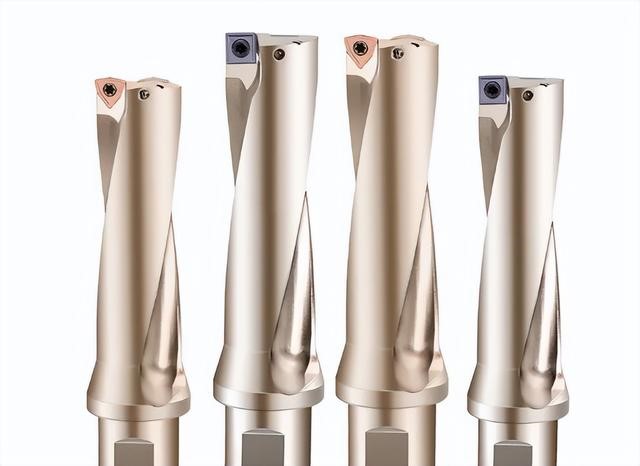

10.Finish-boring tool
Main purpose: precise boring
Features: delicate cutter, high finish, fine adjustment, small cutting volume.

11.Chamfering cutter
Main uses: chamfering C angles, punching points, milling standard small bevels.

12.Inner r cutter
Main purpose: chamfering
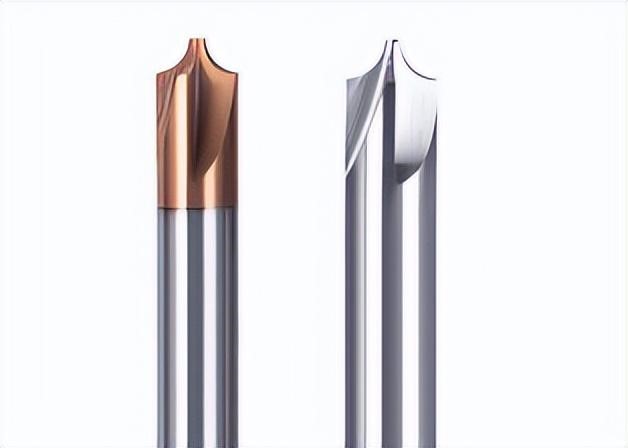

13.Sharp knife (lettering knife, carving knife)
Main uses: carving, lettering, scribing, you can try chamfering, chamfering knife carving.
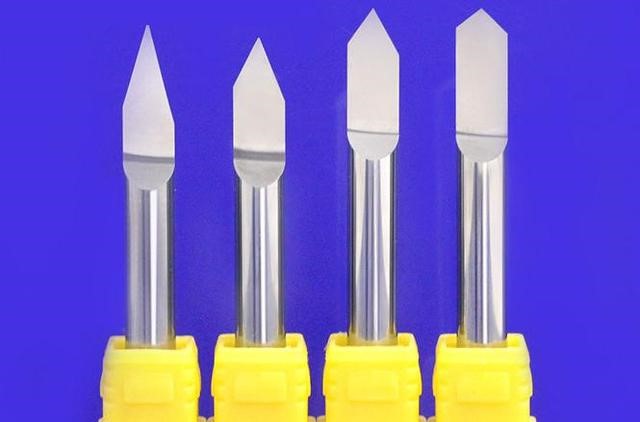

14.T-shaped cutter
Main application: T-slot, inverted buckle machining.
The left side is inlaid T-shaped knife, the right side is one-piece T-shaped knife.
There is also a kind of knife particles, which is better, but the specifications are fewer.

15.Corn milling cutter
Main purpose: roughing, machine strength verifier.
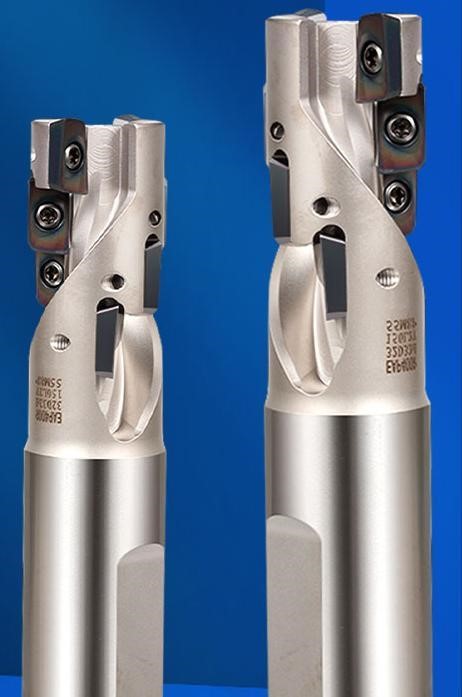

16.Rough boring tools
Main purpose: rough boring, reaming Characteristics: large cutting capacity, suitable for deeper, fixed hole diameter, slightly less accurate.

17.Taper milling cutter
Main purpose: processing standard angle of the beveled surface, you can improve efficiency, do not need to be equal to the height, faster than climbing the surface, to look good, but account for the location of the tool magazine is not universal.
18.Dovetail cutter
Main purpose: processing dovetail groove, back chamfering.

19.Milling cutter
Main purpose: processing of tooth holes, special, deeper, larger tooth holes.

20.Single-edge spiral milling cutter
Main application: processing acrylic, high-density materials.

21.Shaped cutter, customized cutter
Main purpose: processing specific shapes, improve efficiency of the knife, not universal, to be customized, more expensive.
22.Centering bar, also called edge finder
Main purpose: coordinate setting, number finding, position finding, simple assembly, but can realize, high precision results.
The one on the left is an eccentric centering rod.
The one on the right is a buzzer type centering rod.

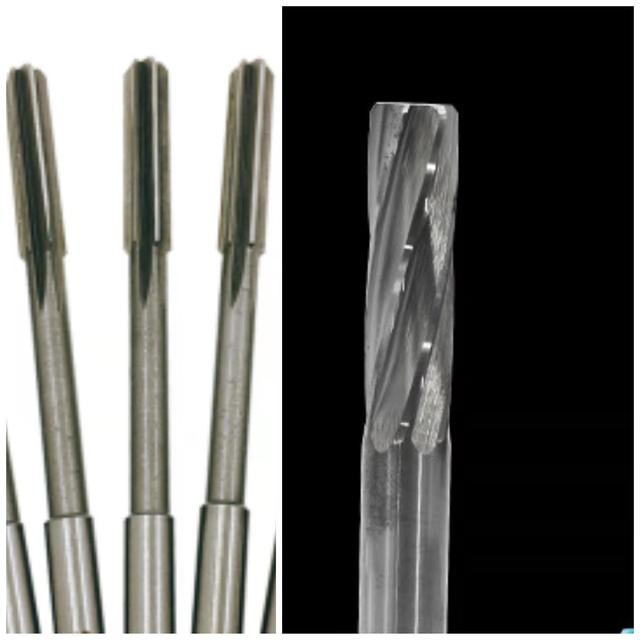
23.Taps
Main use: tapping
24.Reamer
Main applications: machining of fine holes, reaming and reaming of holes, high tool accuracy, pre-drilled holes are required, good stability.


MORE BOLG
Insert mold in injection mold service
What are advantages and disadvantages of Zinc alloy and Aluminum alloy?
Inspection standards for injection molded partappearance
How to judge the quality of your plastic products?
Inspection standards for CNC machining
To ensure that your products are 100% qualified
Categories

Try GREFEE now,for free
We keep your uploaded files confidential and secure.